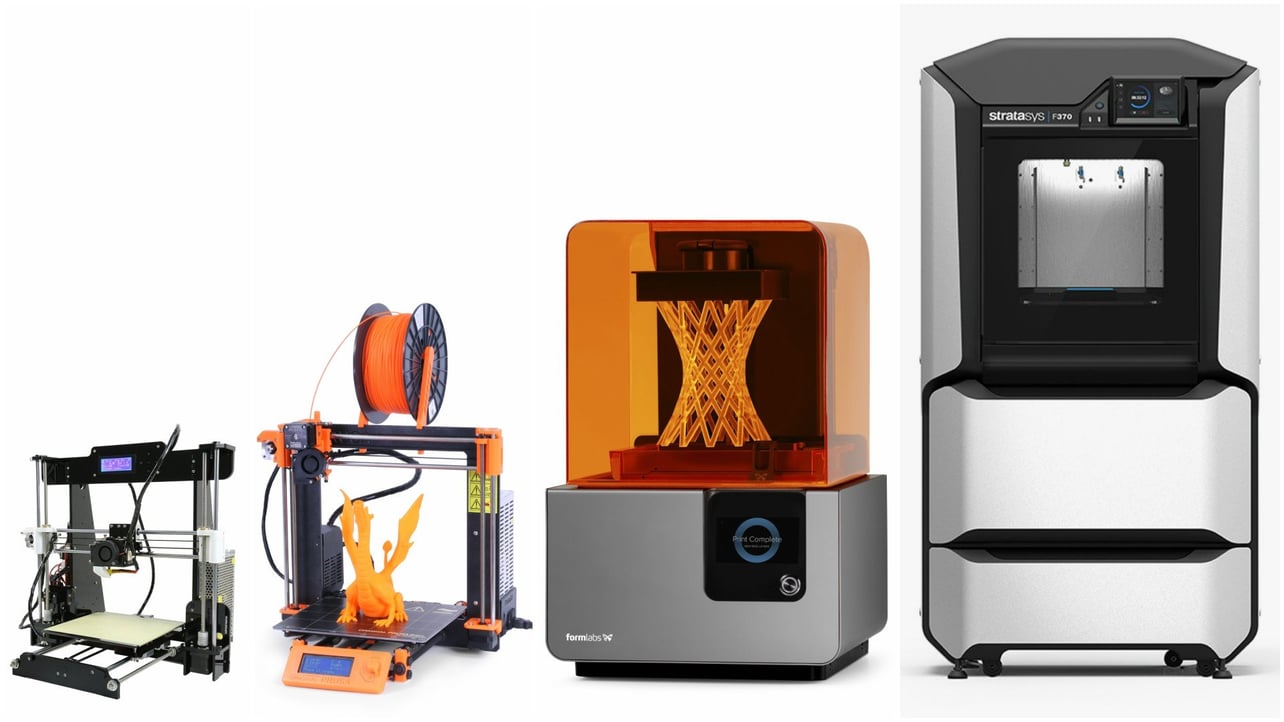
What Does A 3d Printer Do
The creation of a 3d printed object is achieved using additive processes.

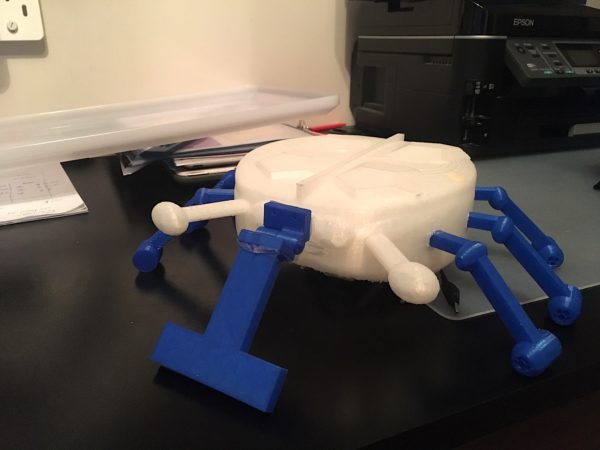
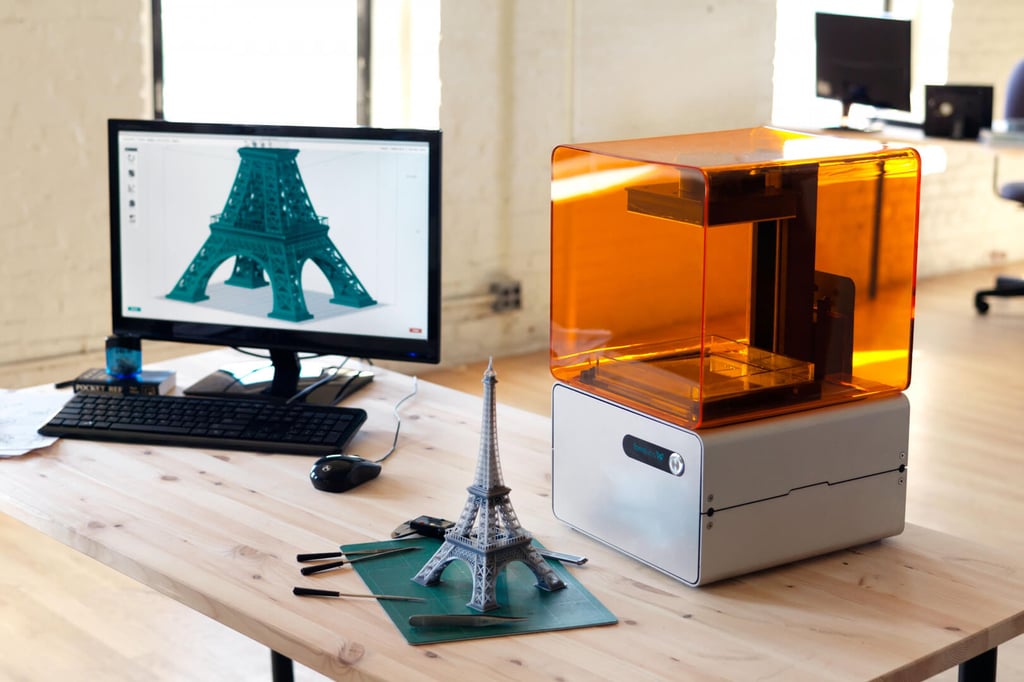
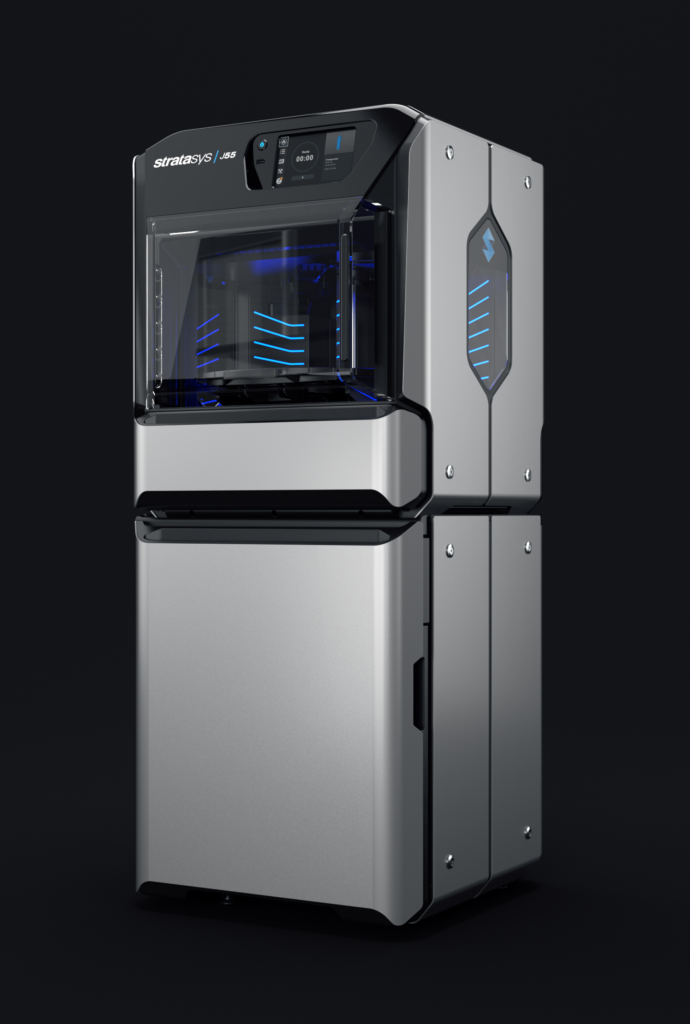
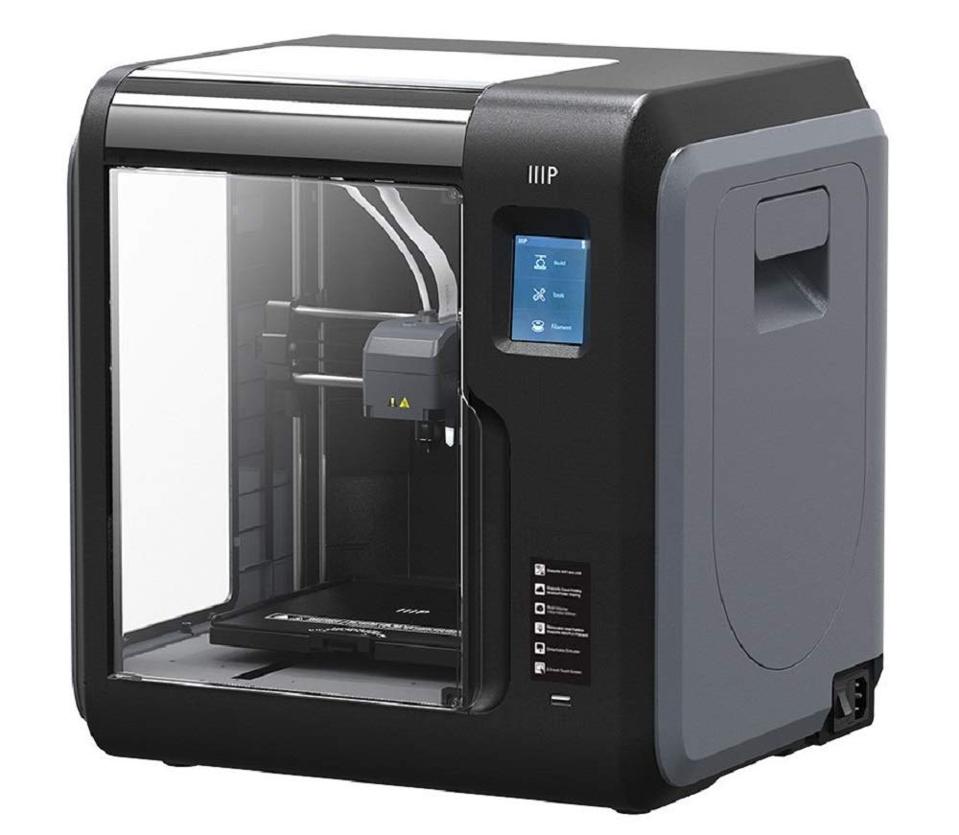
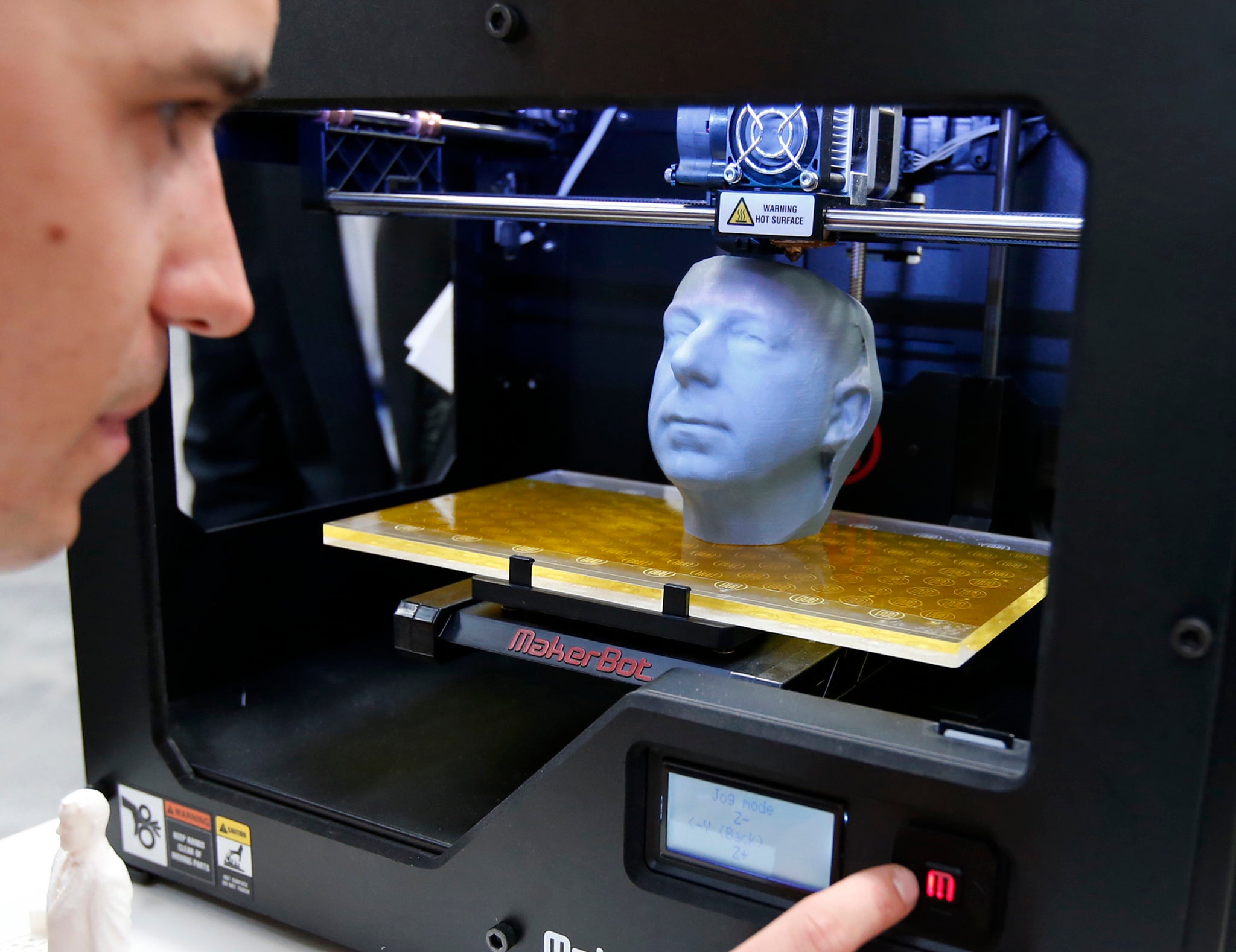
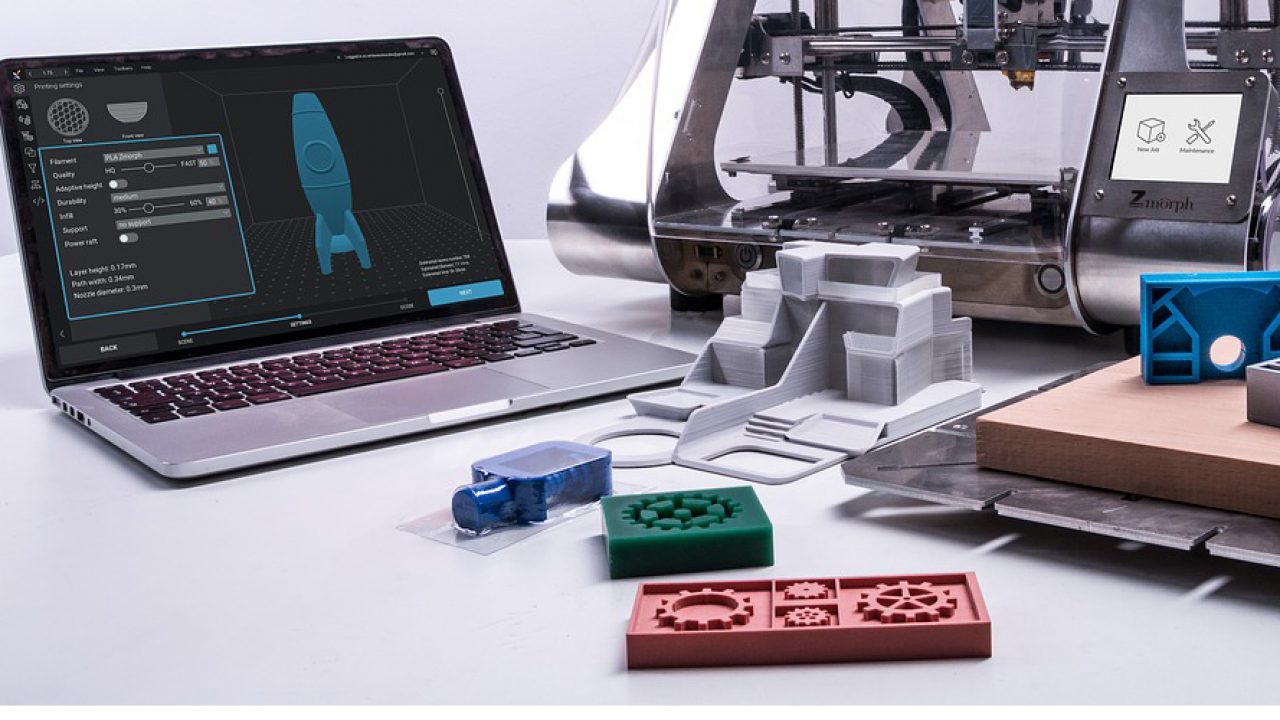
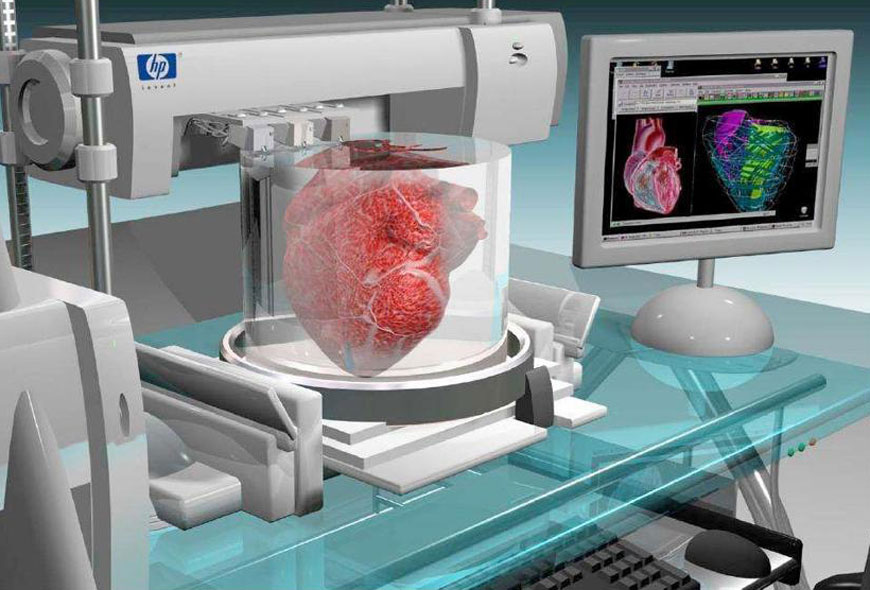
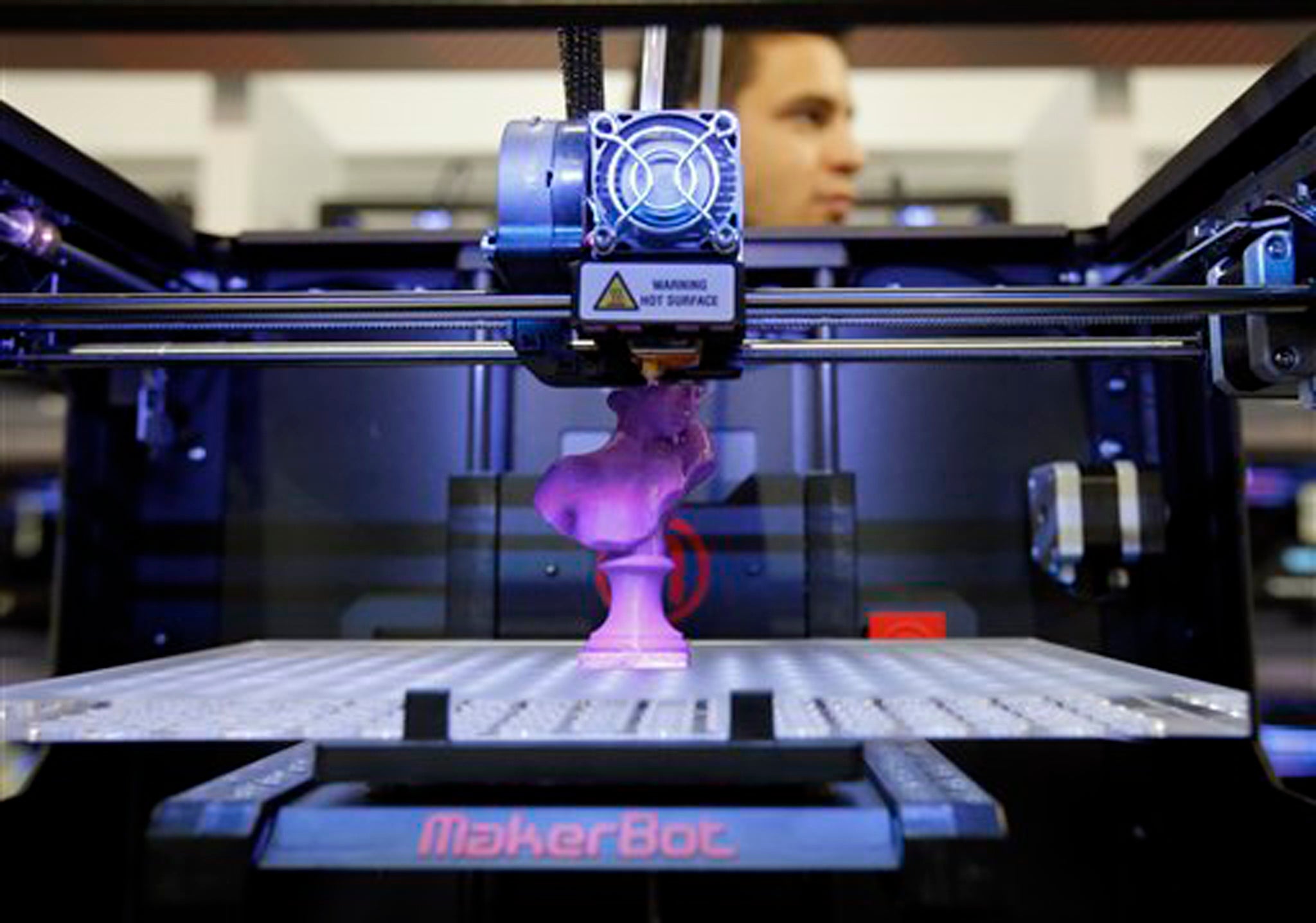
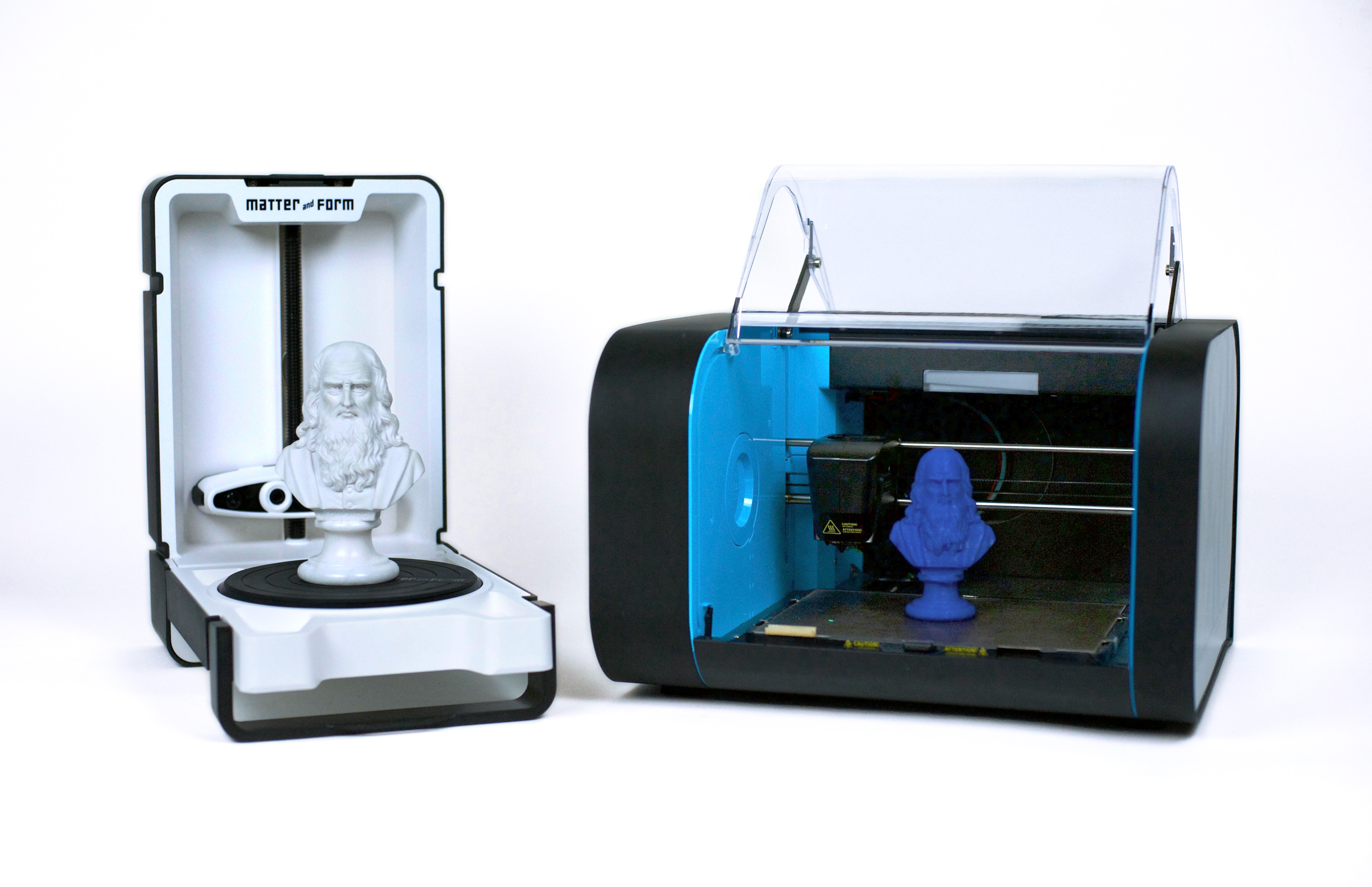
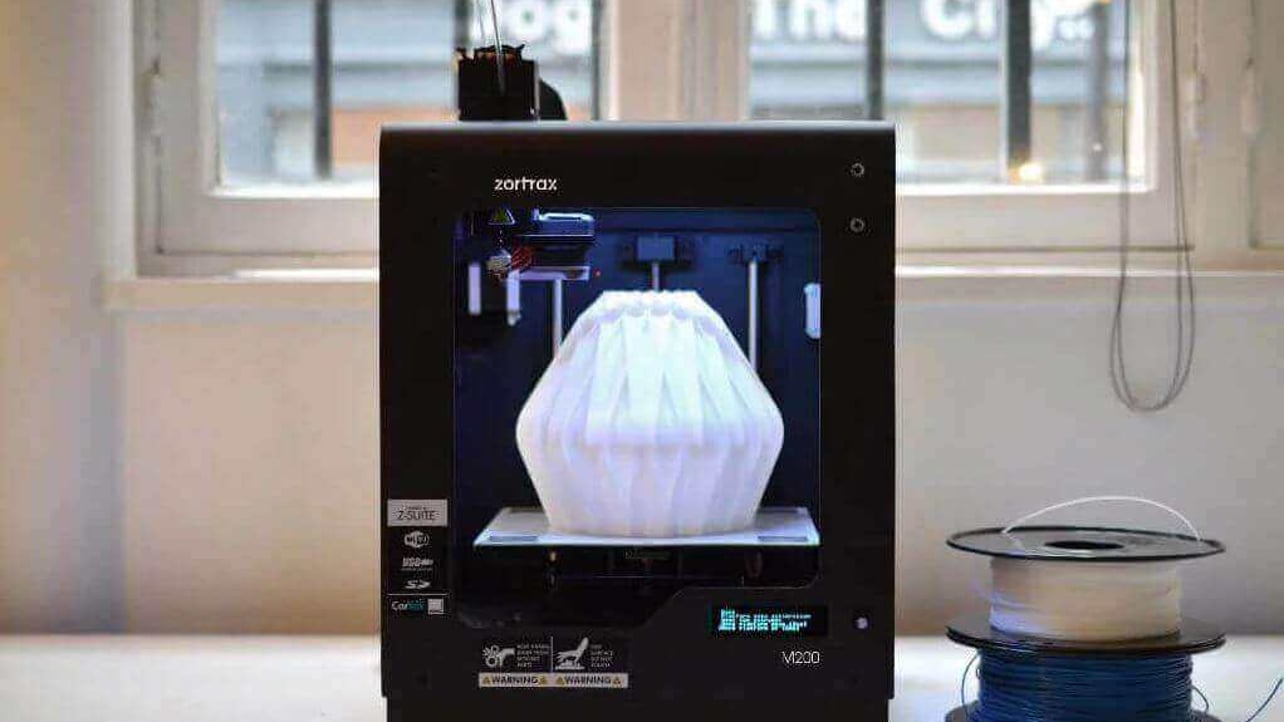
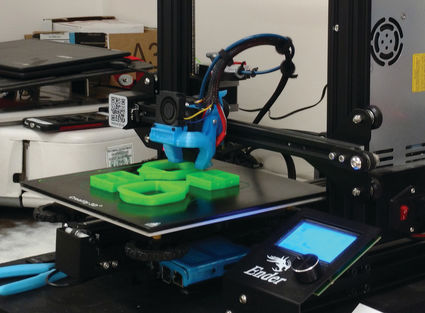
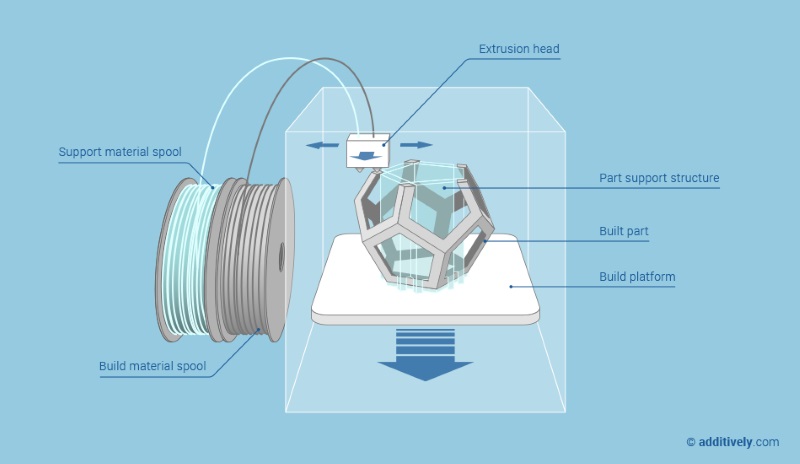
What does a 3d printer do. A 3d printer is a device which given a digital design turns that into a physical object by building up successive layers of material. Fused deposition modeling or fdm is the most common 3d printing process in use as of 2018. In an additive process an object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the object is created. At its most basic 3d printing is a manufacturing process in which material is laid down layer by layer to form a three dimensional object.
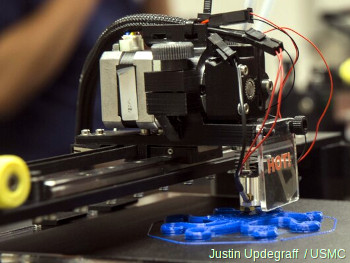
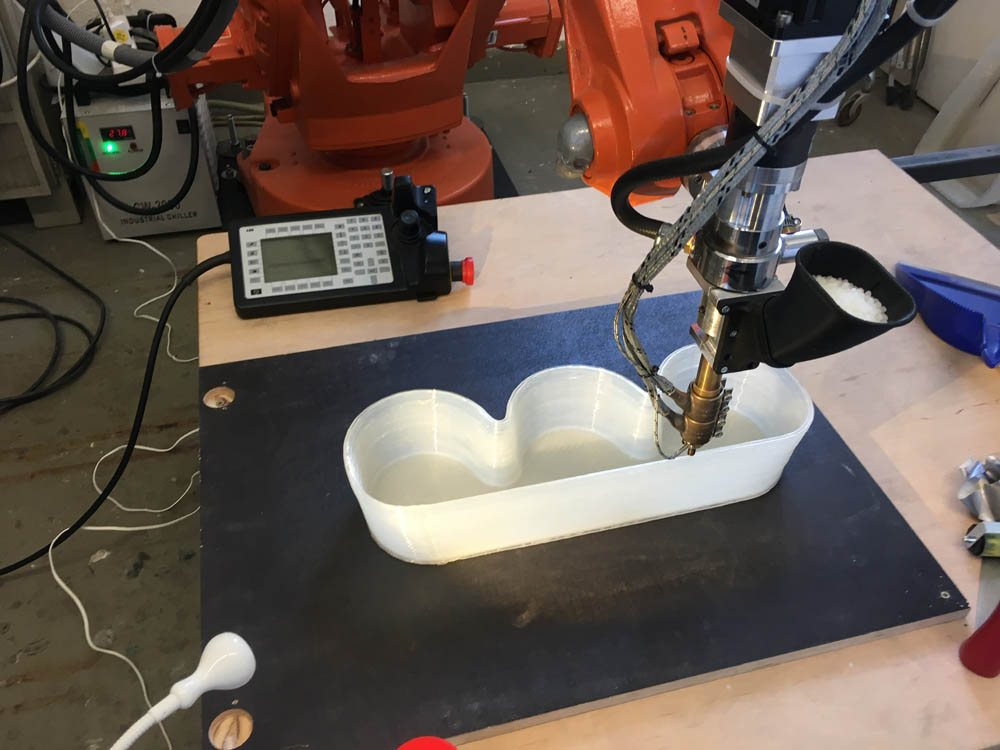
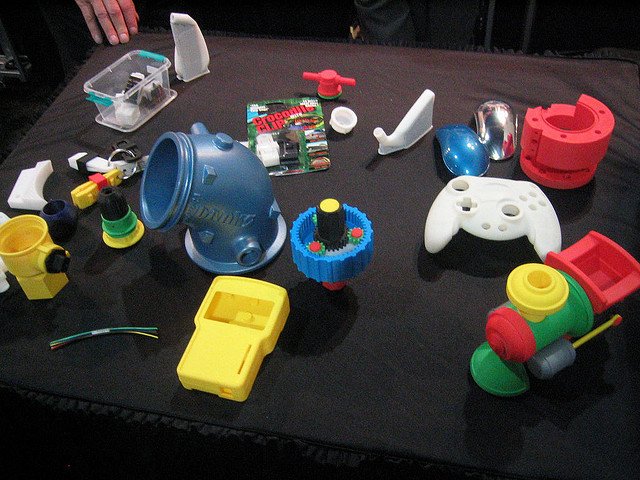
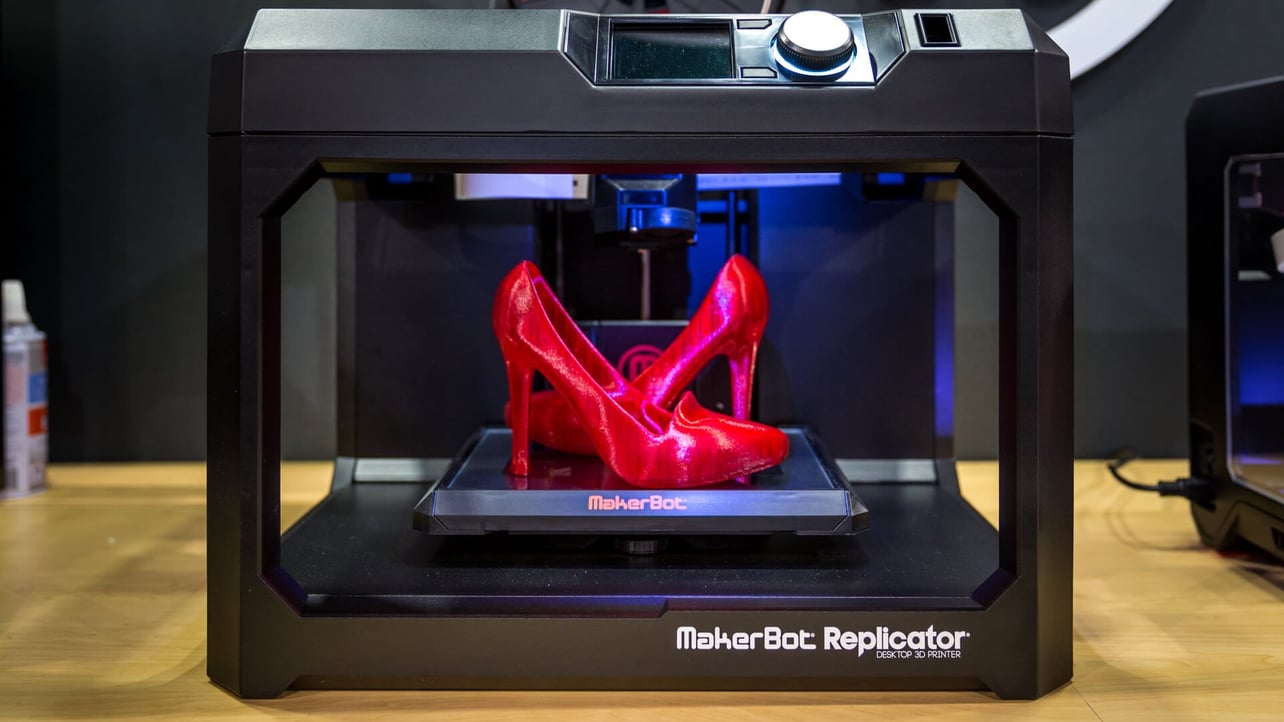
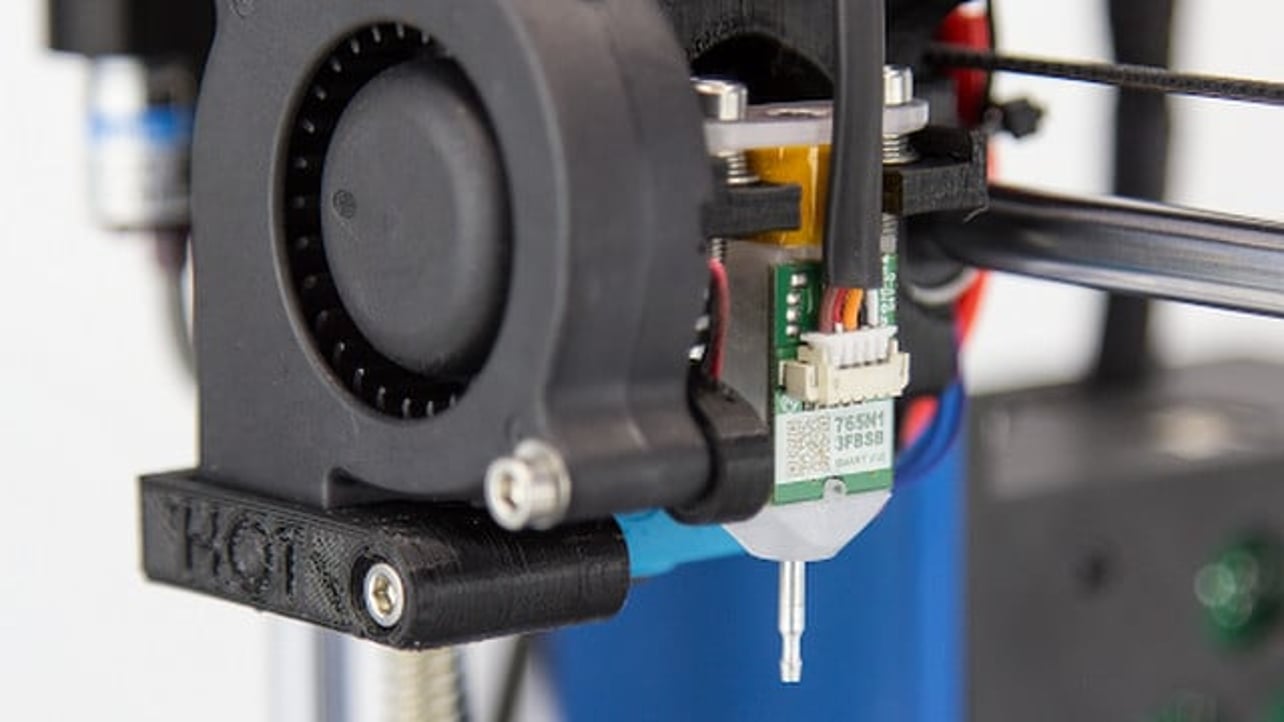
The work is done by a print head able to move freely in three dimensions extruding material initially onto a solid bed and then onto previously printed layers. This is deemed an additive process because the object. Already there are printers available for less than 100. Theyre remarkable because they can produce different kinds of objects in different materials all from the same machine.
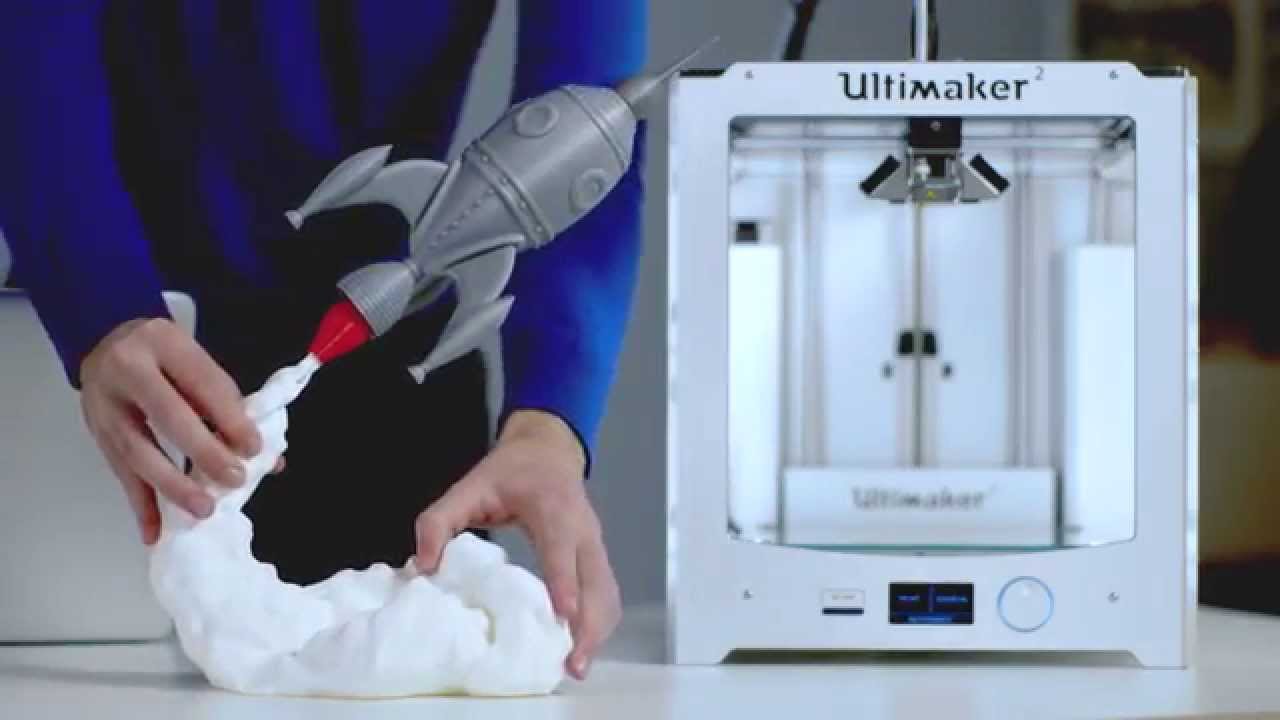
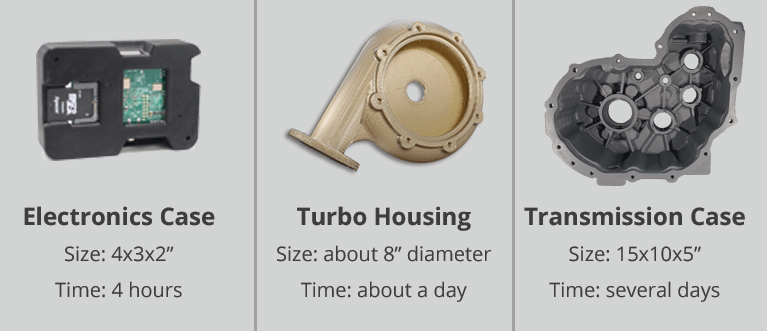
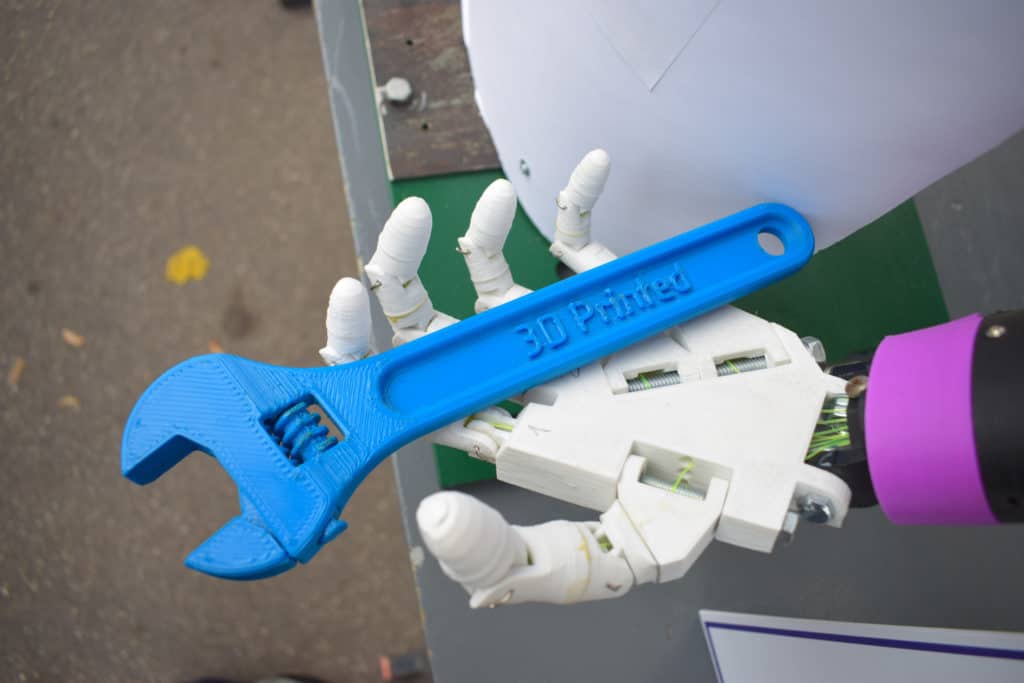
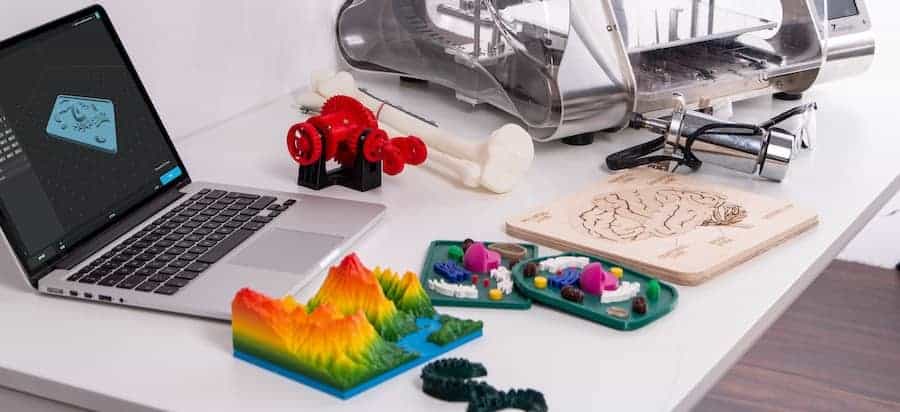
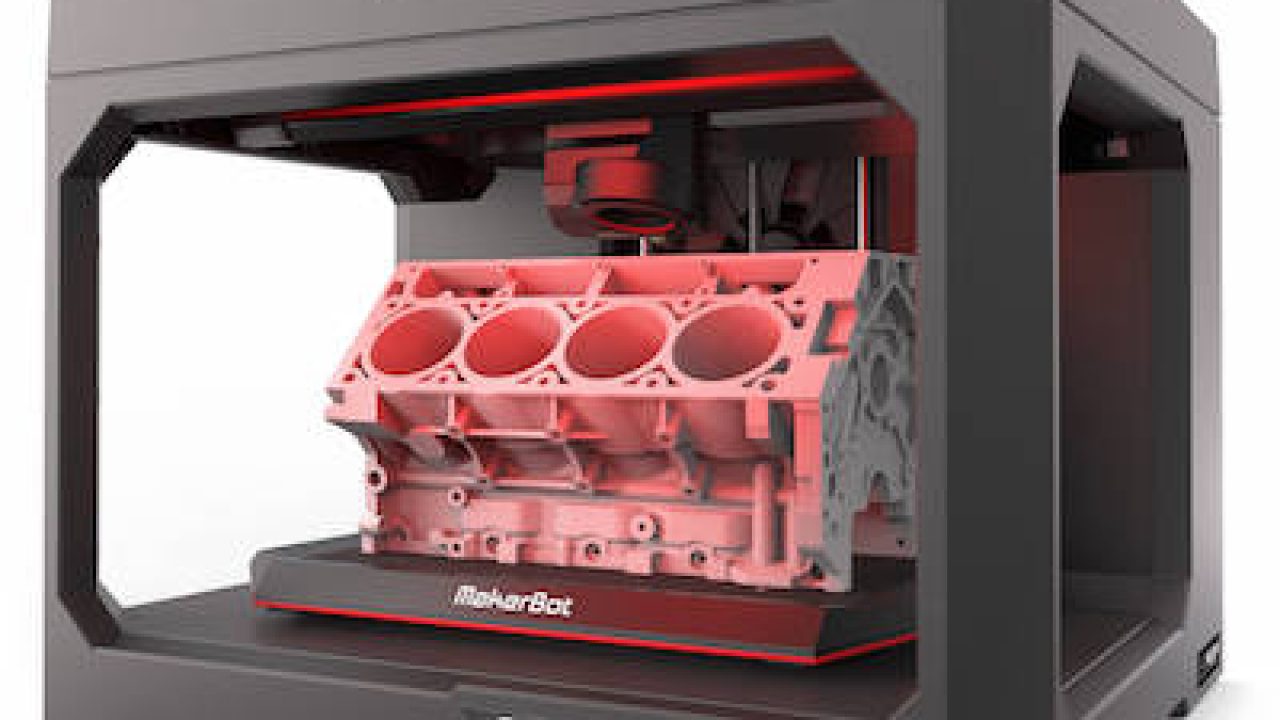
3d printing has had a major impact on the world. It has the potential to transform multiple industries. Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced horizontal cross section of the eventual object. One of the key advantages of 3d printing is the ability to produce very complex shapes or geometries that would be otherwise impossible to construct by hand including hollow parts or parts with internal truss structures to reduce weight.
As the technology behind 3d printers evolves it will become increasingly affordable to simply buy your own home 3d printer. At its core 3d printing is the creation of a three dimensional solid object printed in successive thin layers of material as directed by a digital file you create. 3d printing or additive manufacturing is a process of making three dimensional solid objects from a digital file. It prints one layer waits for it to dry and then prints the next layer on top.












































.jpg)